Why Patents?
Patents protect inventions and ensure the inventors the benefits resulting from the inventions thereby providing incentives for inventiveness, encouraging further inventions and promoting investment. This will spur the economic and technological development. Patent applications already published disclose newly invented technologies and are available for anyone to refer to. They contain vital information for researchers, inventors and enterprises who want to keep up with new developments, carry out R&D activities and use new technologies.
What is a Patent?
The State grants the inventor, by means of a patent, a monopoly, i.e. the right to exclude others from making, using and selling the patented invention for a period of 20 years from the date of application. The owner of the patent can use, or commercialize by selling or licensing the patented technology and derive financial benefits which will contribute to the growth of the economy.
What is an Invention?
An Invention is a practical solution to a problem in the field of technology. An invention may relate to a product or a process.
What can be Patented?
An invention is patentable if it (a) is new (not known in the existing knowledge) (b) industrially applicable (functional and operative) and (c) involves an inventive step (the development or improvement is not obvious to a person of average skill in the particular field.) A patent may be granted to an improvement of a valid patented invention. But when it is being used, there is a possibility of infringing the rights of the owner of the first patent. Therefore, it is advisable to negotiate with the holder of the first patent prior to use.
How a Patent is Granted?
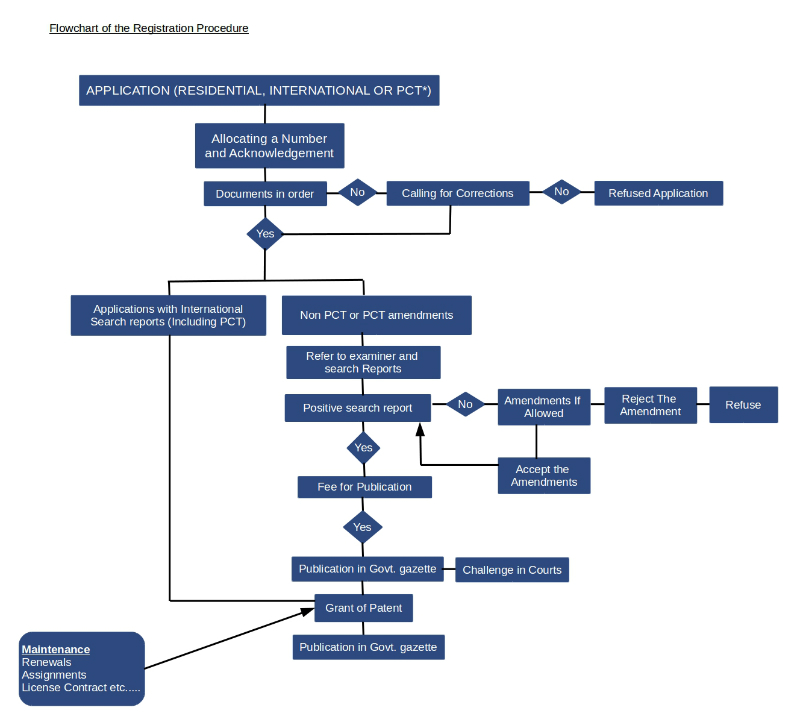
An application can be filed at the National Intellectual Property Office using the prescribed form P1 (refer to the regulations). A document should be submitted with the application form describing the invention clearly and completely along with the claims and the prescribed fee. (refer to the regulations). A search report prepared by an International Searching Authority (ISA) or alternatively, a request can be made to the IP Office to refer the application to a local patent examiner for a search report.
- The IP Office will examine the application and the documents as to the requirements of the IP Act.
- If formal requirements are fulfilled and the application is filed along with relevant documents, the examination will be carried out to ascertain novelty.
- If the patent application fulfills the criteria for patentability, the patent will be granted.
- The accepted applications will be published in the government gazette and patents will be granted, if there are no oppositions against the granting of the Patent.
Renewal
A patent is valid for 20 years from the date of filing. The patent must be renewed annually from the expiration of the second year from the date of grant by paying a fee (please refer to the regulations for fees structure).
What is not patentable?
(i) discoveries, scientific theories and mathematical methods;
(ii) plants, animals micro organisms other than transgenic micro organisms and an essentially biological process for the production of plants and animals other than non biological and micro-biological processes;
(iii) schemes, rules or methods for doing business, performing purely mental acts or playing games
(iv) methods for treatment of human or animal body by surgery or therapy and diagnostic methods practiced on human or animal body
(v) inventions which are necessary to protect public order, morality including human animal or plant life, health, or to avoid serious prejudice to environment.
How to Protect Inventions Abroad?
A patent is valid only in the country where it is granted. As Sri Lanka is a member of the Paris Convention for the protection of industrial property, Sri Lankans can obtain patents for their inventions in any member country of the Paris Convention under the national law of the relevant country. Almost all the countries are members of this convention. Applicant can claim priority under the Paris Convention for the protection of Industrial Property in its member countries which means that claiming the effect of initial filing date in subsequent filing in other member states (if filed within 1 year from the date of application in Sri Lanka).
All Sri Lankan nationals or residents can apply under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) administered by World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in Geneva. You may apply for a patent in many countries (Member Countries of PCT) by filing single application to WIPO. Counties which the applicant intends to file national application later should he designated in the PCT application. PCT filing is a simpler procedure than making several applications in many countries. PCT application has the same effect as a national application filed in the designated countries (For more details log on to www.wipo.int)